Google has announced the release of Gemma 3, the latest and most advanced version of its open-model family. Building on the success of earlier iterations, Gemma 3 introduces key features requested by its community, including multimodal capabilities, extended context windows, and improved multilingual support. The model is available in four sizes—1B, 4B, 12B, and 27B—and can be accessed as pre-trained models for fine-tuning or general-purpose instruction-tuned versions.
Gemma 3 supports vision-language input alongside text outputs, allowing users to interleave images with text for tasks such as image analysis, object identification, and answering questions about visual content. Its integrated vision encoder, based on SigLIP, remains consistent across all model sizes. The model can handle high-resolution and non-square images through an adaptive window algorithm. Additionally, Gemma 3 accommodates context windows of up to 128k tokens and supports over 140 languages with improved math, reasoning, coding, and structured output capabilities.
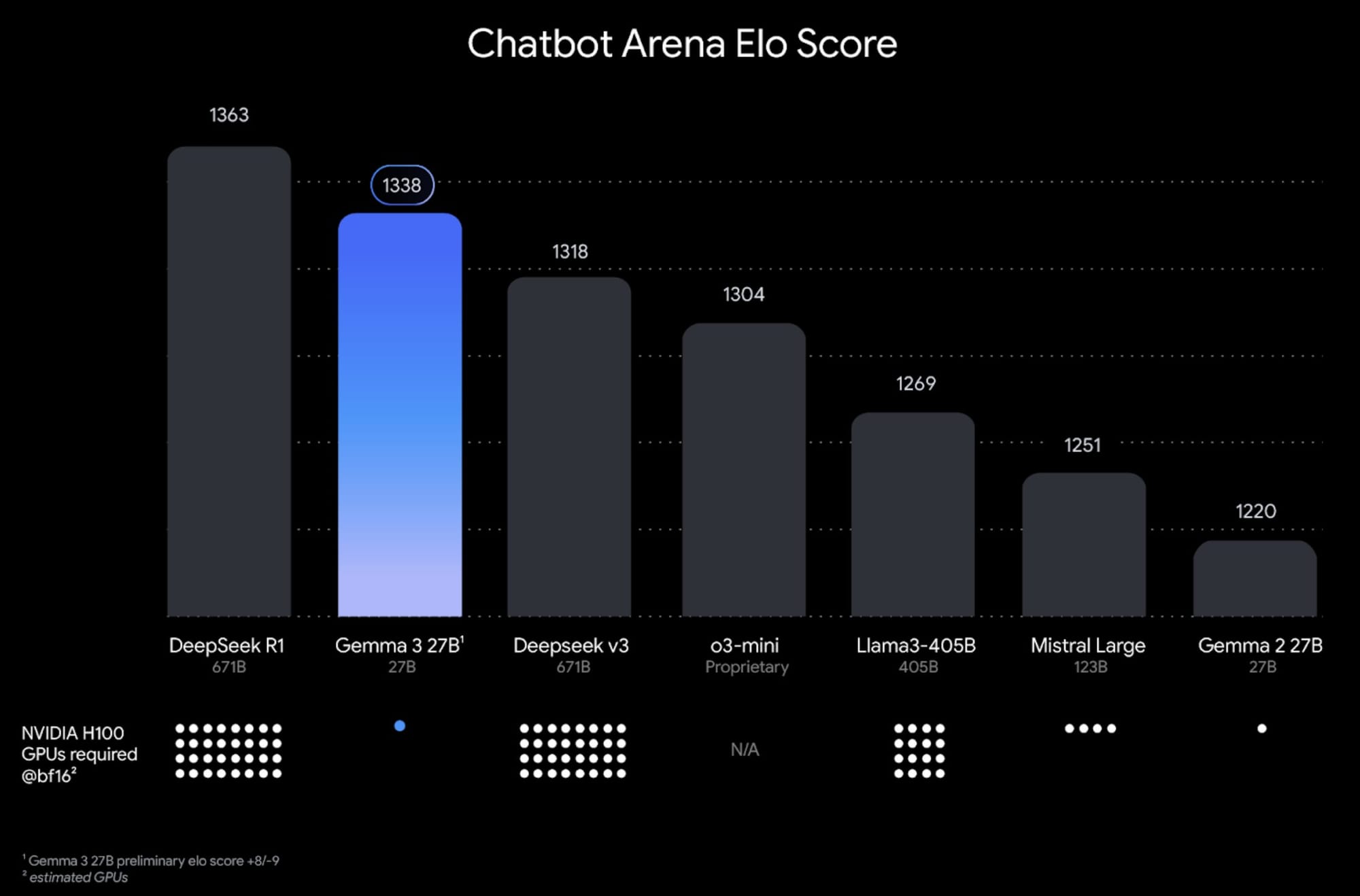
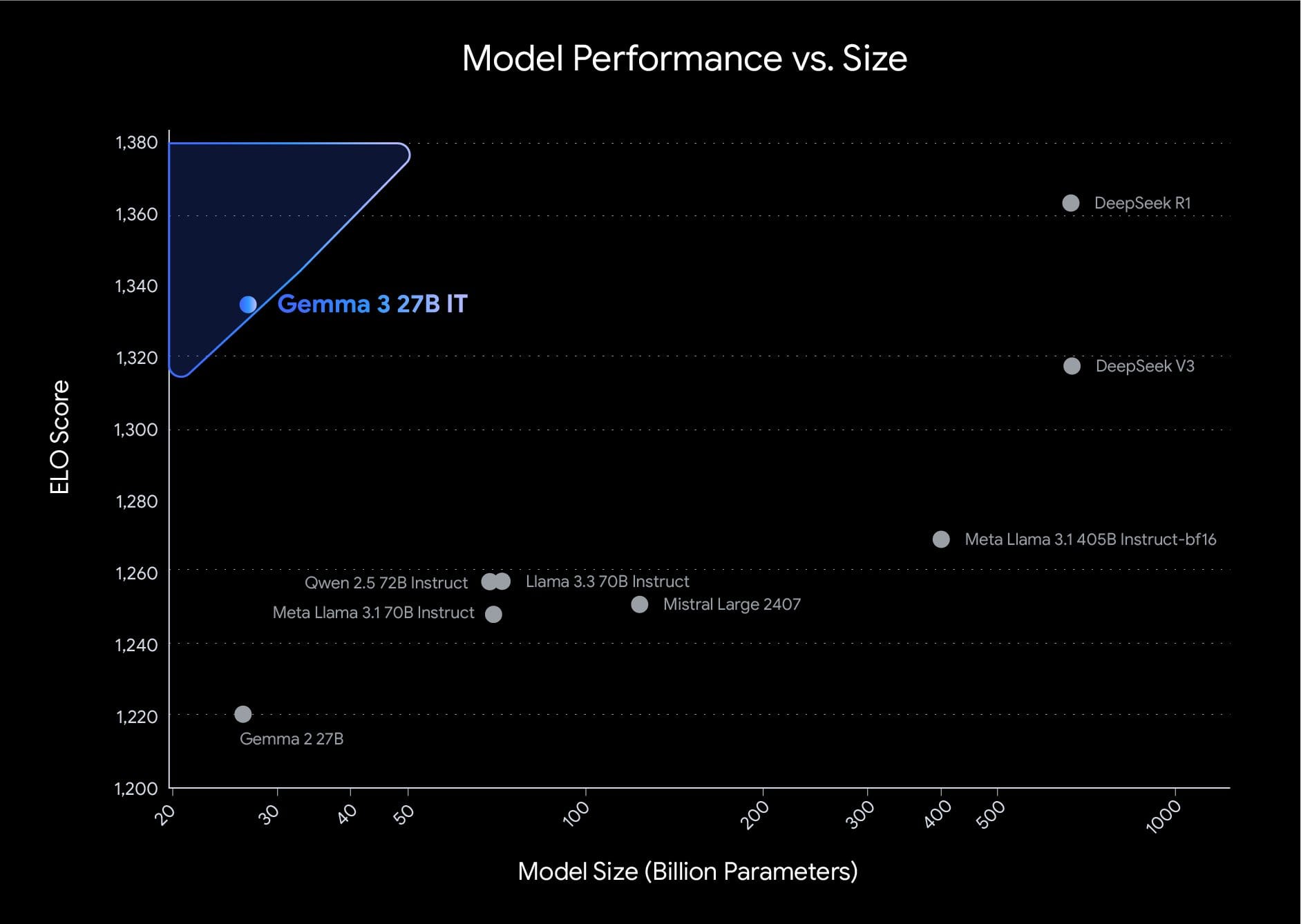
The training process for Gemma 3 involved extensive optimization using distillation, reinforcement learning, and model merging techniques. It was trained on token datasets ranging from 2T to 14T across different sizes using Google TPUs and the JAX framework. A new tokenizer enhances its multilingual functionality. Notably, Gemma 3 achieved the top score of 1338 in LMArena for compact open models.
For safety moderation tasks, Google has introduced ShieldGemma 2—a classifier built on Gemma 3—that labels synthetic and natural images across key safety categories. This tool is particularly useful for filtering inputs in vision-language models like Gemma 3.
The release highlights contributions from the Gemma community, including novel fine-tuning techniques like SimPO from Princeton NLP and unique applications such as OmniAudio by Nexa AI. With over 100 million downloads and more than 60,000 community-created variations since its inception, Gemma continues to expand its impact across diverse domains.