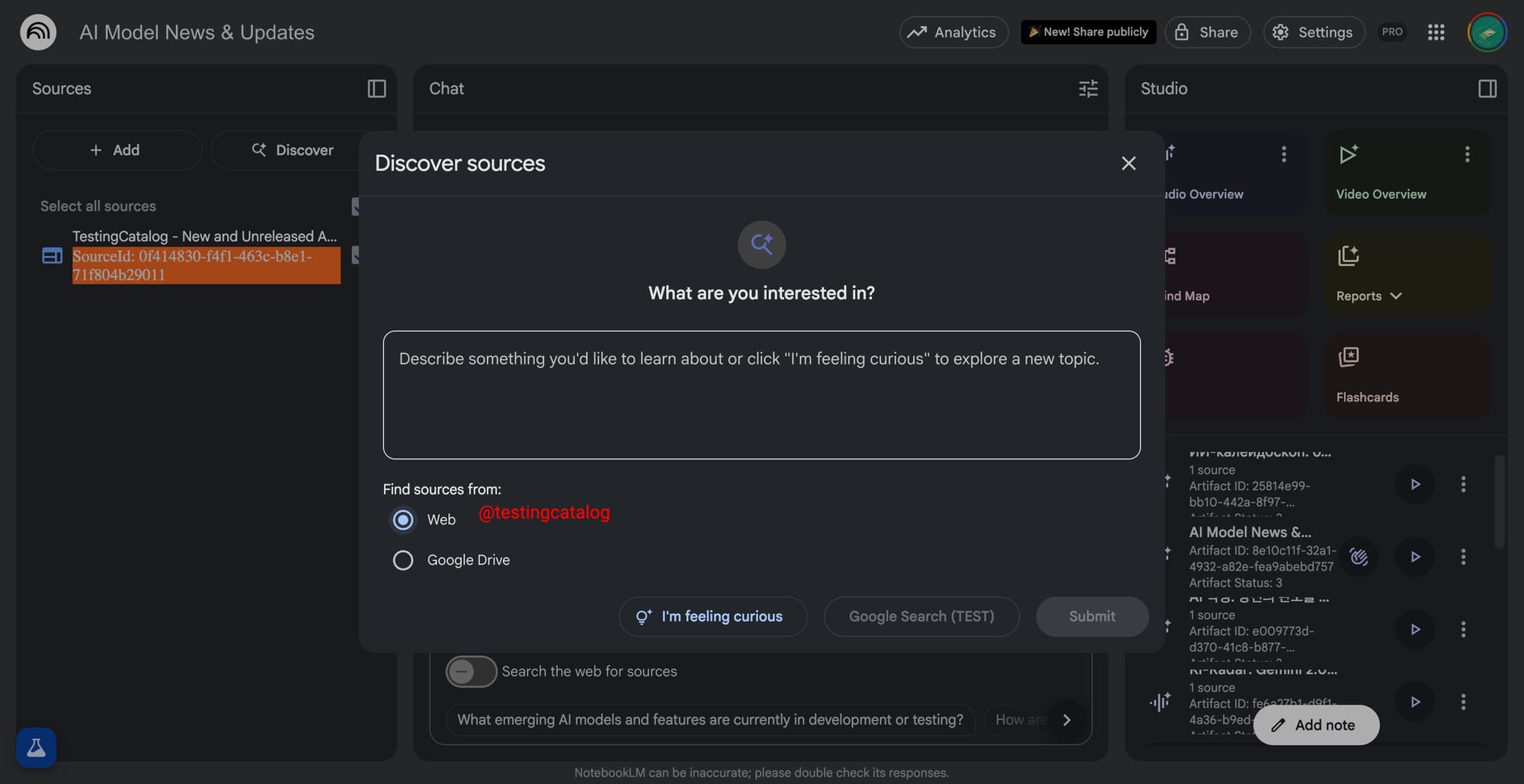
Google is expanding NotebookLM with features that will particularly benefit education and workspace users. The newly discovered “Discover Sources” option for searching across Google Drive will address a major gap for those who store materials in Docs, Slides, and other Drive formats. For organizations and schools relying on Google Workspace, this means NotebookLM will be able to surface relevant internal documents in addition to web content, broadening the scope for research, content synthesis, and corporate knowledge management.
BREAKING 🚨: Google is working on "Flashcards" for NotebookLM and a possibility to discover sources across your Google Drive!
— TestingCatalog News 🗞 (@testingcatalog) June 30, 2025
"Generate AI flashcards based on your sources" pic.twitter.com/vYtzySn25o
A separate addition is the AI Flashcards feature, which will appear in the Studio Panel alongside audio and video overviews. While the full workflow hasn’t been detailed yet, early evidence suggests this feature will let users generate flashcards based on their content, making NotebookLM more valuable for students and lifelong learners.
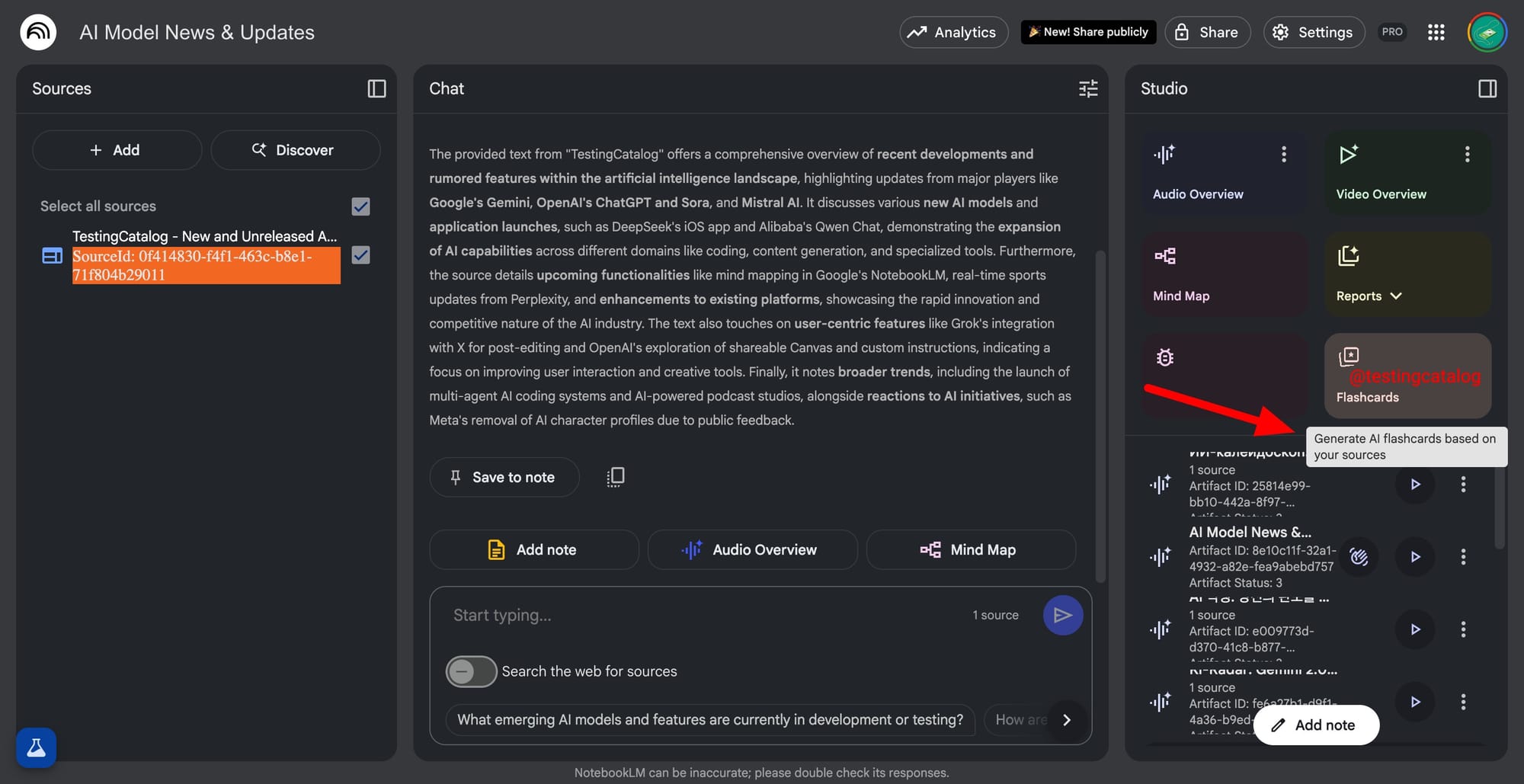
This aligns with Google’s broader strategy of positioning NotebookLM as a central hub for learning, research, and productivity. Flashcards are likely to be interactive, possibly using AI to extract key facts or questions from uploaded materials, turning any document into a study resource.
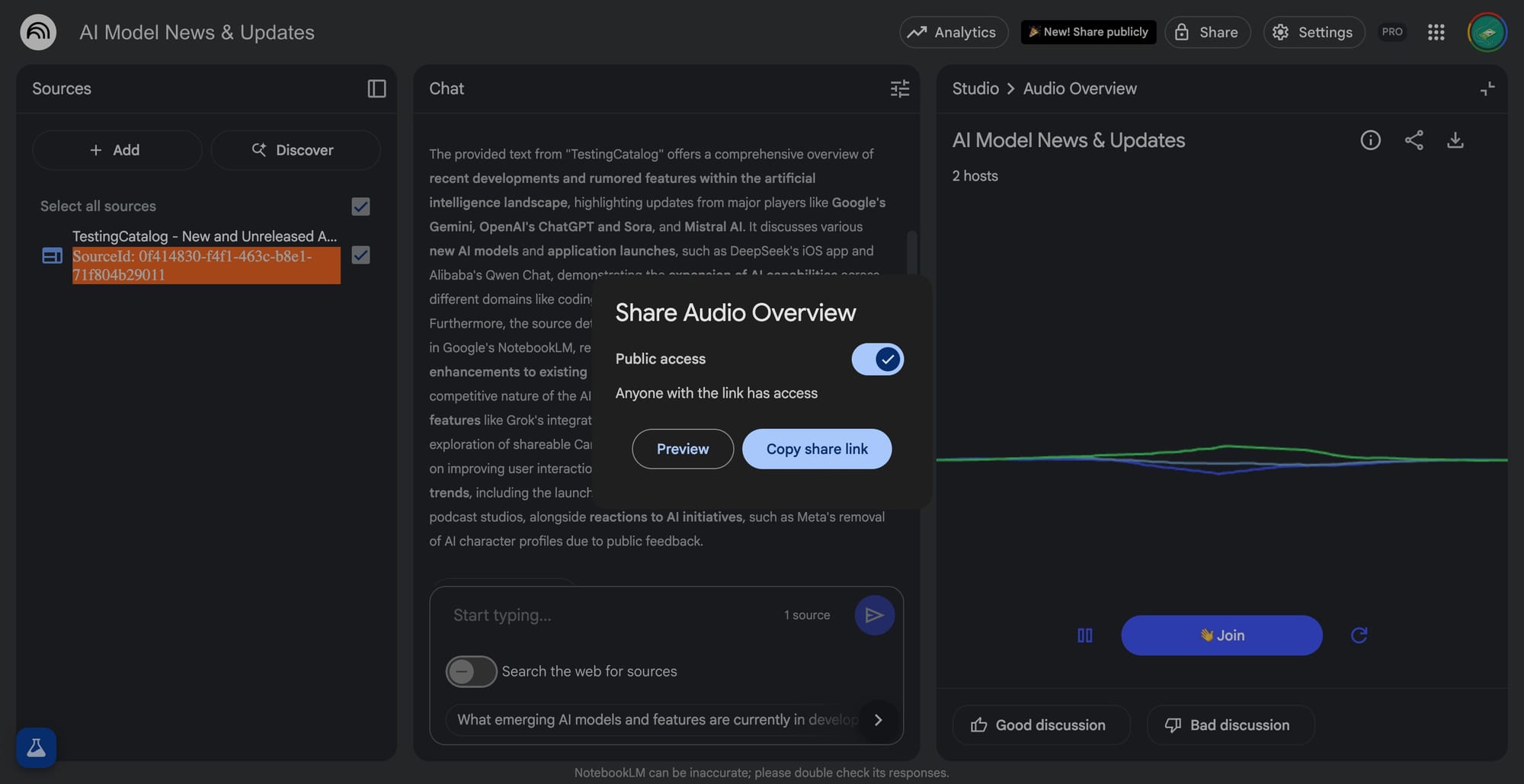
The public sharing of artifacts like audio overviews is now functional, enabling users to distribute individual outputs as public web links. This adds collaborative value, especially for teachers and teams who want to share podcasts or summaries without exposing entire notebooks.
Introducing #Gemini for Education, a version of the @Geminiapp built for you 🫵, the educator! Gemini in Classroom is now free. Plus, find new video overviews in @NotebookLM and quizzes in Gemini. Take a look! 🤠 https://t.co/bbmU8wIAHj #ISTELive2025/#ASCDAnnual25 pic.twitter.com/XuH2CMgZsk
— Google for Education (@GoogleForEdu) June 30, 2025
Video overviews remain unreleased, but their recent mention in Google for Education promotions indicates an official launch could be imminent. These developments signal Google’s intent to make NotebookLM more integrated within its ecosystem, targeting both personal productivity and institutional workflows. The features were identified through analysis of interface updates and internal references, reflecting Google’s incremental approach to feature rollouts.