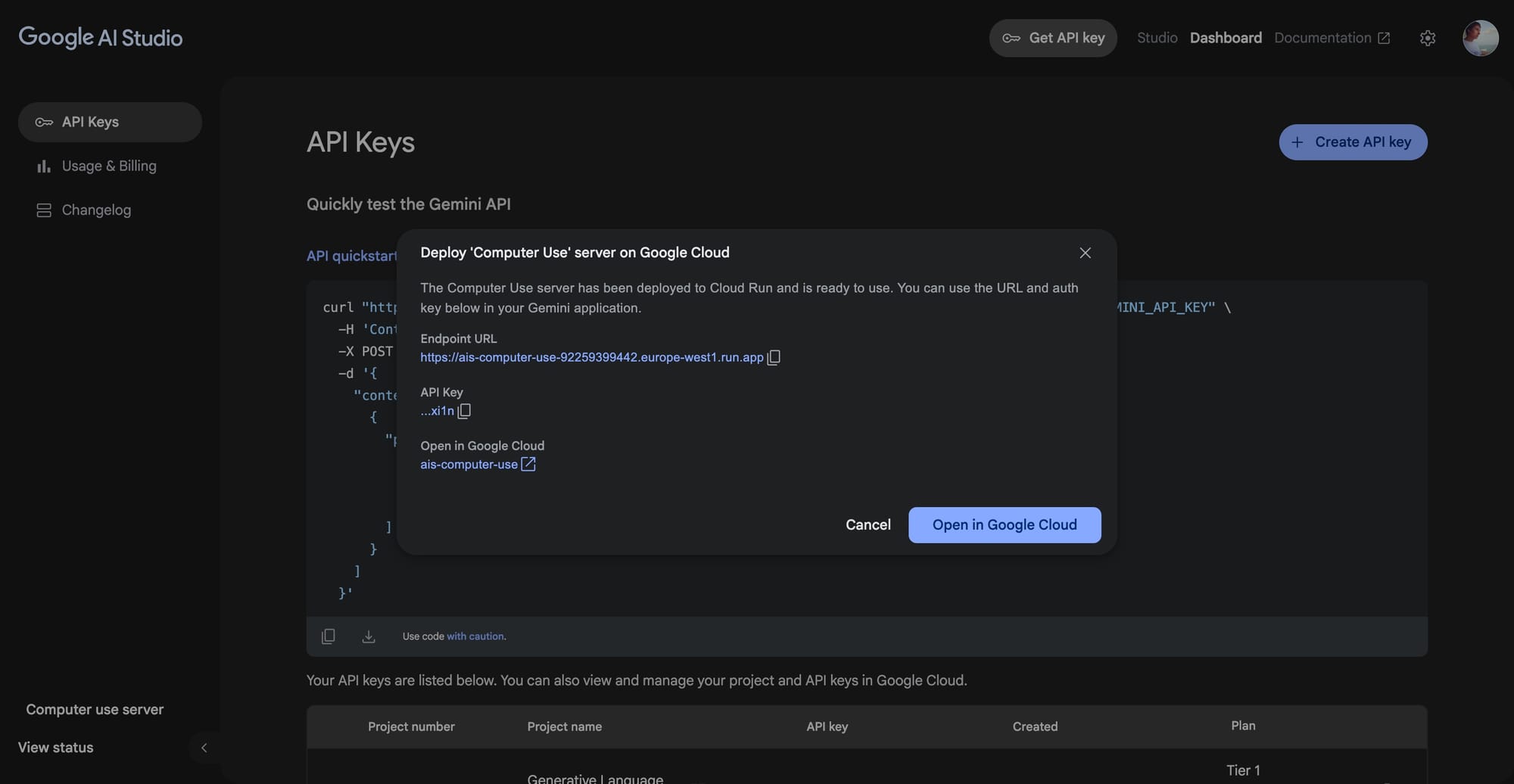
Google appears to be actively expanding the developer-facing capabilities of AI Studio, with new signs pointing toward a feature tentatively called "computer use." Previously, only spotted in backend traces, this capability now reaches the point where interacting with its UI triggers a Cloud Run deployment. The current behavior is limited, users can send an API key through a link to emulate a session, which then spins up a job that remains indefinitely in a "running" state. This incomplete behavior, however, hints at a broader vision: offering sandboxed environments where agents or developers can simulate real browser or OS-level tasks, something comparable to a virtualized operator or autonomous agent interface.
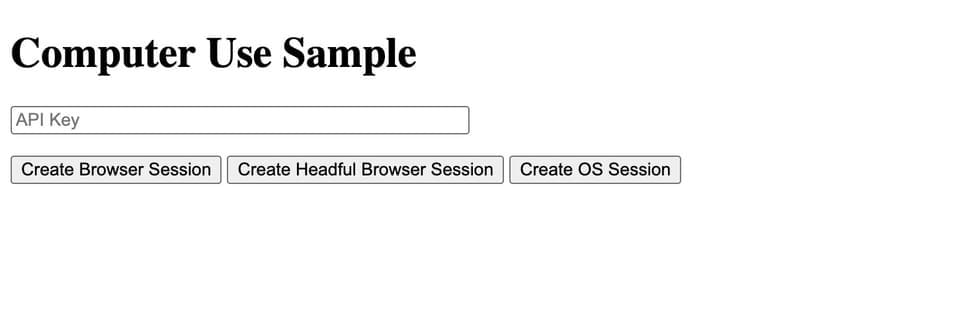
The main beneficiaries of such a capability would be developers building multi-agent systems or workflow tools that require high-fidelity task simulations, such as filling forms, navigating websites, or testing logic in a system context. At this stage, the deployment flow suggests that these sessions are hosted per request, using ephemeral containers via Cloud Run, a pattern suitable for isolated and temporary compute workloads.
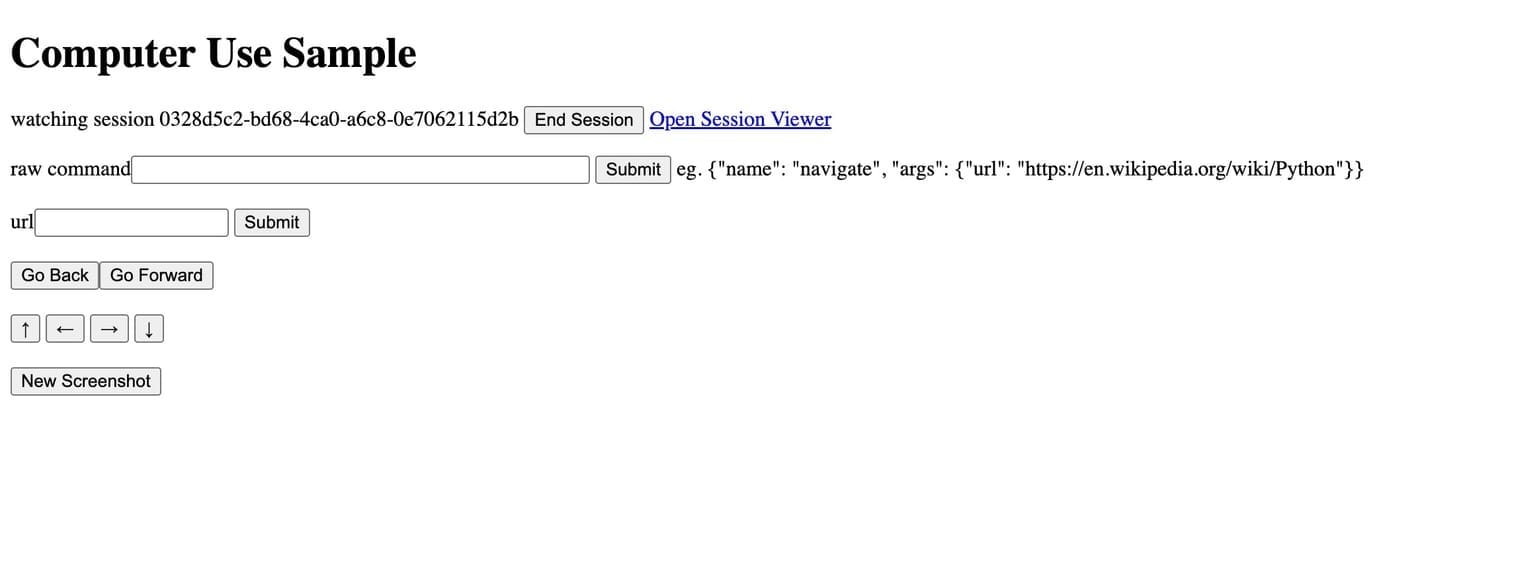
No dedicated model for this use case has been announced by Google, suggesting the company might still be preparing either a custom system model or a specialized variant of Gemini to handle such tasks more reliably. These operator-style capabilities would naturally fit within the long-term strategy of AI Studio as a developer platform, especially as rivals like OpenAI and Perplexity continue investing in autonomous agents.
Altogether, this signals an internal shift toward making AI Studio more of a sandbox for applied AI experimentation rather than just a playground for prompt testing. It's still early, but the infrastructure being scaffolded could become central to Google's broader agent strategy.